The Science Behind Learning And Memory
Learning and memory involve complex processes within the brain. These processes include encoding, storage, and retrieval of information.
The brain’s ability to learn and remember is vital for daily functioning. Neurons communicate through synapses to encode new information. The hippocampus plays a key role in forming new memories. Repetition and practice strengthen neural connections, making recall easier. Sleep also significantly impacts memory consolidation.
A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, supports cognitive function. Understanding these mechanisms can help improve learning strategies and memory retention. Effective learning techniques and memory aids can optimize brain performance. Emphasizing mental health is crucial for maintaining cognitive abilities.

Credit: amplifire.com
Neuroscience Of Learning
The neuroscience of learning explores how the brain processes and retains new information. Our brains are complex and constantly adapting. Understanding the brain’s mechanisms can help improve learning techniques. This section delves into key brain regions and concepts like neuroplasticity.
Brain Regions Involved
Learning involves several brain regions. Each plays a unique role in processing information.
- Hippocampus: This region is crucial for forming new memories.
- Prefrontal Cortex: It handles decision-making and problem-solving.
- Basal Ganglia: It aids in habit formation and motor skills.
- Amygdala: This area processes emotions and emotional memories.
Here’s a simple table summarizing the roles of these brain regions:
| Brain Region | Function |
|---|---|
| Hippocampus | Forms new memories |
| Prefrontal Cortex | Decision-making and problem-solving |
| Basal Ganglia | Habit formation and motor skills |
| Amygdala | Processes emotions and emotional memories |
Neuroplasticity Explained
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to adapt and change. This means our brains can rewire themselves based on new experiences.
There are two types of neuroplasticity:
- Structural Plasticity: The brain physically changes its structure.
- Functional Plasticity: The brain shifts functions from damaged areas to healthy areas.
Key aspects of neuroplasticity include:
- Synaptic Plasticity: Changes in the strength of connections between neurons.
- Neurogenesis: Formation of new neurons in the brain.
Understanding neuroplasticity helps develop better learning strategies. It shows that we can improve our brain’s capabilities through practice and new experiences.
Memory Formation
Memory formation is a fascinating process. It involves encoding, storing, and retrieving information. Our brains work like complex networks, helping us remember things. Understanding this process helps us learn better.
Types Of Memory
There are different types of memory. Each type has a unique role in our lives.
- Short-term memory: This holds information for a brief period.
- Long-term memory: This stores information for a long time.
- Sensory memory: This captures sensory information for a few seconds.
Stages Of Memory
Memory formation occurs in stages. Each stage is crucial for storing information.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Encoding | This is the first stage. It involves converting information into a form our brain can process. |
| Storage | This is the second stage. It involves maintaining the encoded information over time. |
| Retrieval | This is the final stage. It involves accessing stored information when needed. |
Role Of Neurotransmitters
The brain uses chemicals called neurotransmitters to send signals. These chemicals help us learn and remember. Neurotransmitters play a vital role in brain functions. Let’s explore some key neurotransmitters and their impact on learning.
Key Neurotransmitters
Several neurotransmitters affect learning and memory. Here are the most important ones:
- Acetylcholine: Helps in learning and memory formation.
- Dopamine: Related to pleasure and reward. Boosts motivation.
- Serotonin: Affects mood and memory. Helps with focus.
- Glutamate: Main neurotransmitter for learning. Involved in synaptic plasticity.
- GABA: Calms the brain. Prevents overexcitement.
Impact On Learning
Each neurotransmitter has a unique impact on learning:
| Neurotransmitter | Impact on Learning |
|---|---|
| Acetylcholine | Enhances focus and memory. Essential for new information. |
| Dopamine | Increases motivation. Promotes positive reinforcement. |
| Serotonin | Improves mood. Helps maintain attention. |
| Glutamate | Boosts synaptic strength. Key for learning processes. |
| GABA | Reduces anxiety. Balances brain activity. |
Understanding neurotransmitters helps us learn better. It shows how our brain works. Keep these key points in mind for a healthy brain.
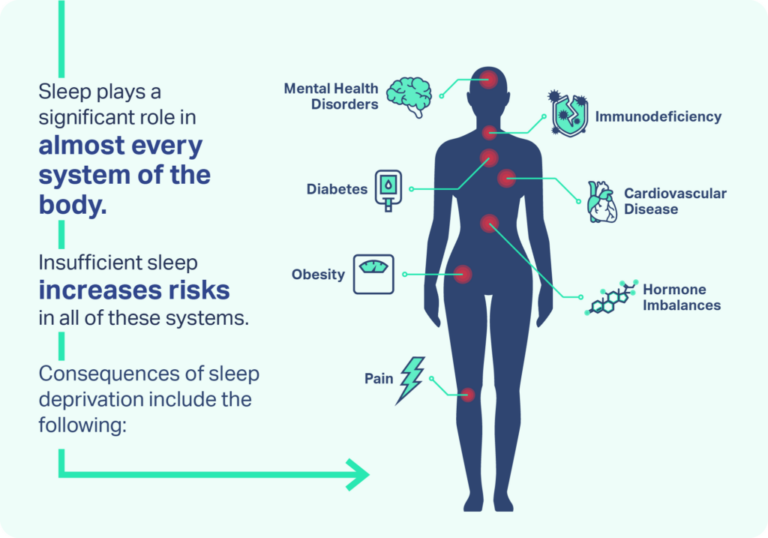
Impact Of Sleep
Sleep plays a crucial role in learning and memory. It helps the brain process new information. Lack of sleep can affect memory and learning abilities.
Sleep Stages
There are different stages of sleep. Each stage is important for memory.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Light sleep. Easy to wake up. |
| Stage 2 | Deeper sleep. Heart rate slows down. |
| Stage 3 | Deep sleep. Hard to wake up. |
| REM | Dreaming stage. Brain activity increases. |
Memory Consolidation
During sleep, the brain organizes new information. This process is called memory consolidation.
- Stage 1: Prepares the brain for deep sleep.
- Stage 2: Helps process simple memories.
- Stage 3: Processes complex memories.
- REM: Strengthens emotional and procedural memories.
Good sleep is essential for learning and memory. It helps the brain function properly. So, always try to get enough sleep.
Emotional Influence
The connection between emotions and memory is a fascinating topic in neuroscience. Emotions can impact how we learn and remember. Positive or negative feelings can make memories stronger.
Emotion And Memory
Emotions play a key role in memory retention. When an event has a strong emotional impact, it is more likely to be remembered. This is because emotions trigger the release of chemicals in the brain, such as norepinephrine and dopamine. These chemicals help in the formation and retention of memories.
Studies show that happy memories are easier to recall. On the other hand, traumatic events can also be vividly remembered. This can sometimes lead to disorders like PTSD.
Here are some ways emotions affect memory:
- Positive emotions: Enhance memory retention
- Negative emotions: Can either enhance or impair memory
- Neutral emotions: Often result in weaker memories
Stress Effects
Stress has a significant impact on learning and memory. Short-term stress can improve memory by releasing adrenaline. This helps the brain to focus and remember details.
Long-term stress, however, can be harmful. It can cause the release of cortisol, which can damage brain cells. This leads to difficulty in forming new memories and recalling old ones.
Here is a table summarizing the effects of stress:
| Type of Stress | Effect on Memory |
|---|---|
| Short-term Stress | Improves memory retention |
| Long-term Stress | Impairs memory formation and recall |
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining a healthy memory. Techniques like meditation, exercise, and proper sleep can help reduce stress levels.
Techniques To Enhance Learning
Learning is a skill that can be improved. Using effective techniques helps in better retention and understanding. This section explores some proven methods to enhance learning and memory.
Active Learning
Active learning engages the mind. It requires participation and interaction. This method includes:
- Asking questions during lessons
- Participating in discussions
- Solving problems
- Applying concepts in real-life scenarios
Active learning makes information stick. It transforms passive listening into engaging activities. This approach helps in better comprehension and recall.
Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition is a memory technique. It involves reviewing information at increasing intervals. This method helps in long-term retention. Here’s a simple plan:
- Review new information on the same day
- Revisit the material the next day
- Review again after one week
- Check the content after one month
Spaced repetition combats the forgetting curve. It ensures information is moved to long-term memory. This technique is highly effective for learning new concepts.
| Technique | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Active Learning | Engages mind, improves comprehension, enhances recall |
| Spaced Repetition | Long-term retention, combats forgetting, effective for new concepts |
Nutrition And Brain Health
Understanding the connection between nutrition and brain health is crucial. Our brain needs the right nutrients to function at its best. Eating well can boost memory, focus, and overall cognitive function.
Essential Nutrients
The brain needs certain nutrients to stay healthy and sharp. These include:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. They support brain cell structure.
- Antioxidants: Found in berries, nuts, and dark chocolate. They protect the brain from damage.
- Vitamins: Vitamins B6, B12, and E are vital. They support brain function and prevent cognitive decline.
- Minerals: Iron and magnesium are important. They help in oxygen transport and nerve function.
Dietary Tips
Here are some tips for a brain-friendly diet:
- Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables. They provide essential vitamins and antioxidants.
- Include fish in your diet. Fish like salmon are rich in Omega-3 fatty acids.
- Snack on nuts and seeds. They are great sources of healthy fats and antioxidants.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains. Whole grains have more nutrients and fiber.
- Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water to keep your brain functioning properly.
Sample Brain-boosting Meal Plan
| Meal | Food |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts |
| Lunch | Grilled salmon with quinoa and steamed veggies |
| Snack | Apple slices with almond butter |
| Dinner | Chicken stir-fry with brown rice |

Credit: snoozemattresscompany.com
Technological Aids
Technology has revolutionized the way we learn and remember. It offers tools that enhance our educational experiences. Let’s explore some key technological aids that help in learning and memory.
Educational Tools
Educational tools have transformed the learning landscape. These tools are designed to make learning engaging and effective. Here are some popular educational tools:
- Interactive Whiteboards: They allow teachers to display content dynamically.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Khan Academy offer various subjects.
- eBooks: Digital books make it easy to access and read anywhere.
These tools offer visual aids, quizzes, and interactive lessons. They help students grasp concepts quickly.
Cognitive Apps
Cognitive apps are designed to boost brain functions. They target memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Let’s look at some popular cognitive apps:
- Lumosity: This app offers games that improve memory and attention.
- Elevate: Elevate focuses on skills like reading, writing, and math.
- Peak: Peak provides personalized brain training exercises.
These apps use scientific methods to enhance cognitive abilities. They are user-friendly and easy to integrate into daily routines.
The combination of educational tools and cognitive apps creates a powerful learning environment. It helps users retain information better and boosts overall cognitive health.

Credit: www.learning.com
Conclusion
Understanding the science behind learning and memory can transform how we approach education and personal growth. By leveraging these insights, we can enhance our cognitive abilities. Remember, continuous practice and a healthy lifestyle are key. Stay curious and keep exploring new ways to boost your brain power.