The Impact of Genetics on Personal Health
Genetics significantly influences personal health by determining susceptibility to various diseases. It also affects responses to medications and treatments.
Genetic makeup plays a crucial role in shaping individual health outcomes. Genes, inherited from parents, carry information that dictates physical traits and biological processes. This genetic blueprint impacts everything from the risk of developing chronic conditions like diabetes and heart disease to how one metabolizes drugs.
Understanding genetic predispositions allows for personalized healthcare strategies, enabling more effective prevention and treatment plans. Advances in genetic research have made it possible to identify specific genes linked to health issues, offering insights into tailored medical interventions. By considering genetic factors, healthcare providers can enhance patient care and improve overall health outcomes.
Credit: aihms.in
Genetics And Health
Understanding the impact of genetics on personal health is crucial. Genetics influence many aspects of health. They determine traits, disease risks, and responses to treatments. This knowledge helps in personalizing healthcare. Let’s explore the key concepts and roles of genetics in disease.
Basic Concepts
Genes are the building blocks of life. They are made of DNA. Genes carry instructions for making proteins. These proteins perform specific functions in the body.
Humans have about 20,000 to 25,000 genes. Each person has two copies of each gene, one from each parent. Variations in these genes are called alleles. Alleles can be beneficial, harmful, or neutral.
Genetic variations can affect health. Some variations cause diseases. Others increase or decrease disease risks. Understanding these variations helps in predicting health outcomes.
Role In Disease
Genetics play a major role in many diseases. Some diseases are directly caused by gene mutations. These are known as genetic disorders.
- Cystic Fibrosis: Caused by mutations in the CFTR gene.
- Sickle Cell Anemia: Caused by mutations in the HBB gene.
- Huntington’s Disease: Caused by mutations in the HTT gene.
Other diseases are influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors. These are known as complex diseases.
- Heart Disease: Influenced by genes and lifestyle choices.
- Diabetes: Affected by genetic and environmental factors.
- Obesity: Results from genes and diet.
Genetics also influence how individuals respond to medications. This field is called pharmacogenomics.
| Medication | Gene | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Warfarin | CYP2C9 | Affects drug metabolism |
| Statins | SLCO1B1 | Impacts drug uptake |
| Codeine | CYP2D6 | Influences drug activation |
Understanding genetic influences on health can lead to better treatments. It helps in developing personalized medicine. This approach tailors treatments to individual genetic profiles.
Genetic Disorders
Genetic Disorders are health problems caused by changes in our genes. These changes can be inherited or happen spontaneously. Understanding these disorders helps us better manage and treat our health.
Inherited Conditions
Some genetic disorders are passed down from parents to children. These are called inherited conditions. They occur when parents pass on faulty genes.
- Cystic Fibrosis: Affects lungs and digestive system.
- Sickle Cell Anemia: Causes red blood cells to be misshapen.
- Hemophilia: Leads to excessive bleeding due to clotting issues.
Each of these conditions can have a significant impact on personal health. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve quality of life.
Mutations And Variants
Sometimes, genetic disorders are not inherited. They result from mutations or variants in our DNA. These changes can happen randomly or due to environmental factors.
- Down Syndrome: Caused by an extra chromosome 21.
- Turner Syndrome: Affects females, missing an X chromosome.
- Fragile X Syndrome: Linked to intellectual disabilities.
Mutations can occur at any stage of life. Not all mutations lead to disorders, but some can cause serious health issues.
| Disorder | Type | Main Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Cystic Fibrosis | Inherited | Affects lungs and digestion |
| Down Syndrome | Mutation | Extra chromosome 21 |
| Turner Syndrome | Mutation | Missing X chromosome |
Understanding how genetic disorders occur helps in developing treatments. It also aids in managing these conditions better.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine, also known as precision medicine, tailors medical treatment to individual characteristics. This approach considers a person’s genetic makeup, environment, and lifestyle. By understanding genetic differences, doctors can provide more effective treatments. Personalized medicine is revolutionizing healthcare, making it more efficient and tailored.
Tailored Treatments
Tailored treatments offer unique benefits for patients. Doctors can create specific treatment plans based on genetic information. This reduces the risk of side effects and increases treatment success. For example, cancer treatments can be customized to target specific genetic mutations. This leads to better outcomes and fewer complications.
Here are some key advantages of tailored treatments:
- Improved Accuracy: Treatments are designed to match individual genetic profiles.
- Fewer Side Effects: Personalized plans reduce adverse reactions.
- Increased Effectiveness: Targeted therapies work better for specific conditions.
Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics studies how genes affect a person’s response to drugs. This field helps doctors choose the right medication and dosage. By understanding genetic variations, doctors can avoid ineffective treatments. Pharmacogenomics ensures patients receive the most effective drugs for their genetic makeup.
Benefits of pharmacogenomics include:
- Optimized Drug Selection: Choose the best medication for each patient.
- Reduced Trial and Error: Minimize the guesswork in finding effective treatments.
- Enhanced Safety: Lower the risk of adverse drug reactions.
Here is a table summarizing the differences between traditional and personalized medicine:
| Traditional Medicine | Personalized Medicine |
|---|---|
| One-size-fits-all approach | Customized to individual genetics |
| Higher risk of side effects | Lower risk of side effects |
| Trial-and-error method | Targeted and precise treatments |
Genetic Testing
Genetic Testing is a powerful tool in understanding our health. It involves analyzing DNA to identify changes or mutations. These changes can affect our risk for certain diseases. This knowledge can help us make better health choices.
Types Of Tests
There are different types of genetic tests. Each serves a unique purpose. Here are some common types:
- Diagnostic Testing: Identifies genetic disorders in symptomatic individuals.
- Predictive Testing: Assesses risk for developing certain diseases.
- Carrier Testing: Determines if a person carries a gene for a recessive disorder.
- Prenatal Testing: Detects changes in a fetus’s genes before birth.
- Newborn Screening: Tests newborns for genetic disorders early on.
Pros And Cons
Genetic testing has its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding both helps in making informed decisions.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Provides valuable health information | May cause anxiety or stress |
| Helps in disease prevention | Results can be uncertain or unclear |
| Guides personalized treatment plans | Potential for genetic discrimination |
| Informs family planning decisions | Privacy concerns with genetic data |
Ethical Considerations
Understanding the impact of genetics on personal health brings many ethical considerations. These considerations are crucial for safeguarding individuals’ rights and ensuring fairness. This section explores the major ethical concerns, focusing on privacy issues and discrimination risks.
Privacy Issues
Genetic information is highly personal and sensitive. It can reveal much about an individual’s health, heritage, and potential future conditions. Protecting this data from unauthorized access is critical. Unauthorized access can lead to misuse and breaches of confidentiality.
Healthcare providers and genetic testing companies must follow strict privacy laws. These laws ensure that genetic data is stored securely and shared responsibly. Individuals should be fully aware of how their genetic data will be used and stored.
A table illustrating privacy laws and protections can be helpful:
| Privacy Law | Protection Offered |
|---|---|
| HIPAA | Protects health information and ensures data confidentiality |
| GDPR | Regulates data protection and privacy in the EU |
| CCPA | Gives California residents rights over their personal data |
Discrimination Risks
Discrimination based on genetic information is a real concern. Employers and insurers might misuse genetic data to make biased decisions. This can lead to unfair treatment of individuals with certain genetic traits.
Laws like the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA) protect against such discrimination. GINA prevents employers and insurers from using genetic data to discriminate. Despite these protections, vigilance is essential.
An ordered list of steps to combat discrimination risks includes:
- Educate individuals about their rights under GINA.
- Promote awareness about genetic discrimination issues.
- Encourage reporting of discrimination incidents.
- Support legislation that strengthens genetic data protections.
Individuals should know their rights and report any violations promptly. Education and awareness are key to preventing genetic discrimination.
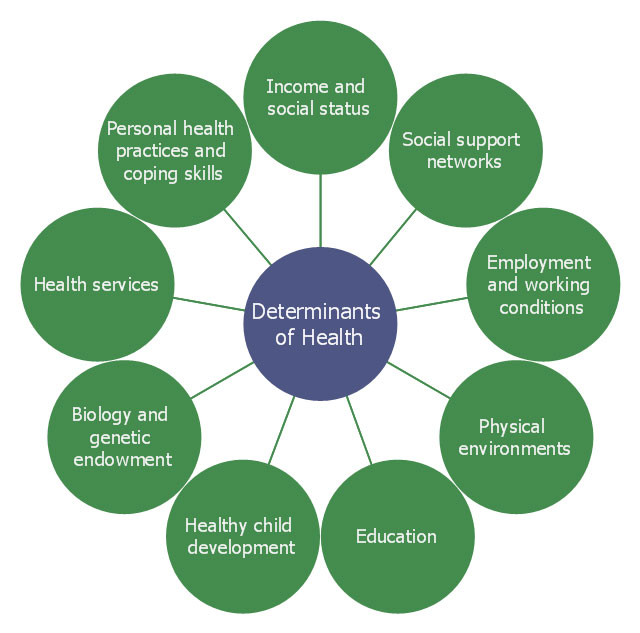
Lifestyle And Genetics
Our lifestyle choices and genetics together shape our health. Understanding this connection helps us make better decisions for our well-being. Lifestyle factors like diet and exercise interact with our genes. This affects how we feel and function every day.
Diet And Nutrition
Diet and nutrition play a key role in our health. Our genes can influence how we process different foods. Some people may need more vitamins or minerals than others. Eating a balanced diet is important for everyone. Here are some tips to consider:
- Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables.
- Include whole grains in your diet.
- Choose lean proteins like fish and chicken.
- Limit sugary snacks and drinks.
Exercise And Fitness
Exercise and fitness are crucial for staying healthy. Genetics can influence how our bodies respond to different types of exercise. Some people may excel at endurance sports. Others might be better at strength training. Regular exercise benefits everyone. Here are some exercise tips:
- Find activities you enjoy, like swimming or biking.
- Exercise for at least 30 minutes each day.
- Mix cardio, strength, and flexibility exercises.
- Stay active with friends or family.
Preventive Measures
Genetics play a crucial role in personal health. Understanding your genetic makeup can help in taking preventive measures. These measures can improve overall well-being and reduce health risks.
Early Detection
Early detection is key to managing genetic risks. Genetic testing can identify potential health issues before symptoms appear. This allows for timely intervention and treatment.
Health screenings should be a regular part of your routine. These can catch diseases early and improve treatment outcomes. Regular check-ups with your doctor are essential.
| Screening Type | Recommended Age |
|---|---|
| Breast Cancer Screening | Age 40+ |
| Prostate Cancer Screening | Age 50+ |
| Genetic Testing for Heart Disease | Any Age |
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can significantly reduce genetic health risks. Simple habits can make a big difference in your health.
- Healthy Diet: Eat fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes a day.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking increases risks of many diseases.
- Limit Alcohol: Drink in moderation to stay healthy.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
These changes are easy to implement and can improve your health. Start today and see the benefits over time.

Credit: stop.publichealth.gwu.edu
Future Of Genetic Research
The future of genetic research holds immense promise. Our understanding of genes continues to grow. This will drastically change personal health. The next few years will bring exciting developments.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are driving genetic research forward. They help us understand our genes better. Here are some key technologies:
- CRISPR: This tool allows precise gene editing.
- Next-generation sequencing: It reads DNA quickly and cheaply.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI analyzes genetic data faster.
CRISPR can edit genes to fix mutations. Next-generation sequencing helps identify genetic disorders early. AI predicts health issues based on genetic data.
Potential Breakthroughs
Many potential breakthroughs are on the horizon. These could transform how we approach health.
| Breakthrough | Impact |
|---|---|
| Personalized Medicine | Treatments tailored to your genetic makeup. |
| Gene Therapy | Cures for genetic disorders. |
| Predictive Genetics | Early detection of potential health issues. |
Personalized medicine means treatments are designed for you. Gene therapy might cure diseases like cystic fibrosis. Predictive genetics can catch problems before they start.
The future of genetic research is bright. These advancements will improve health for everyone.

Credit: pged.org
Conclusion
Understanding genetics offers insights into personal health. Tailored healthcare becomes possible with genetic information. Embrace genetic knowledge to make informed health decisions. Genetics can improve our well-being and future health outcomes. Stay proactive and explore your genetic profile for better health.