The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Health
Sleep deprivation severely impacts health, leading to cognitive impairment and an increased risk of chronic diseases. It affects mental and physical well-being.
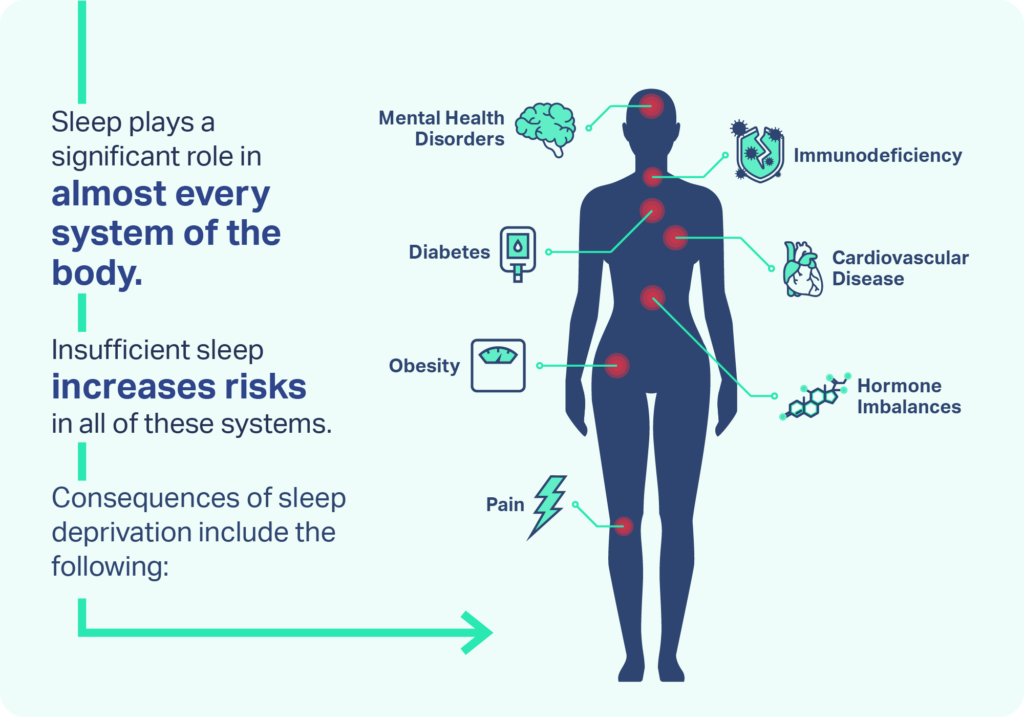
Quality sleep is essential for maintaining optimal health. Lack of adequate sleep disrupts cognitive functions, making it hard to concentrate and remember information. Chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of serious health conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. It weakens the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Mood disorders such as depression and anxiety are also linked to poor sleep. Ensuring sufficient and quality sleep can significantly enhance overall health and well-being. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene and establishing a regular sleep schedule can mitigate these adverse effects.
Effects On Mental Health
Sleep deprivation has a profound impact on mental health. Inadequate sleep can lead to various psychological issues. This section explores the effects of sleep deprivation on mental health.
Mood Disorders
Sleep deprivation often triggers mood disorders. People may feel irritable and stressed. They may also experience anxiety and depression. A lack of sleep disrupts emotional regulation.
Here’s a brief look at the connection between sleep and mood:
- Irritability: Less sleep makes people more irritable.
- Anxiety: Sleep-deprived individuals often feel anxious.
- Depression: Chronic sleep loss can lead to depression.
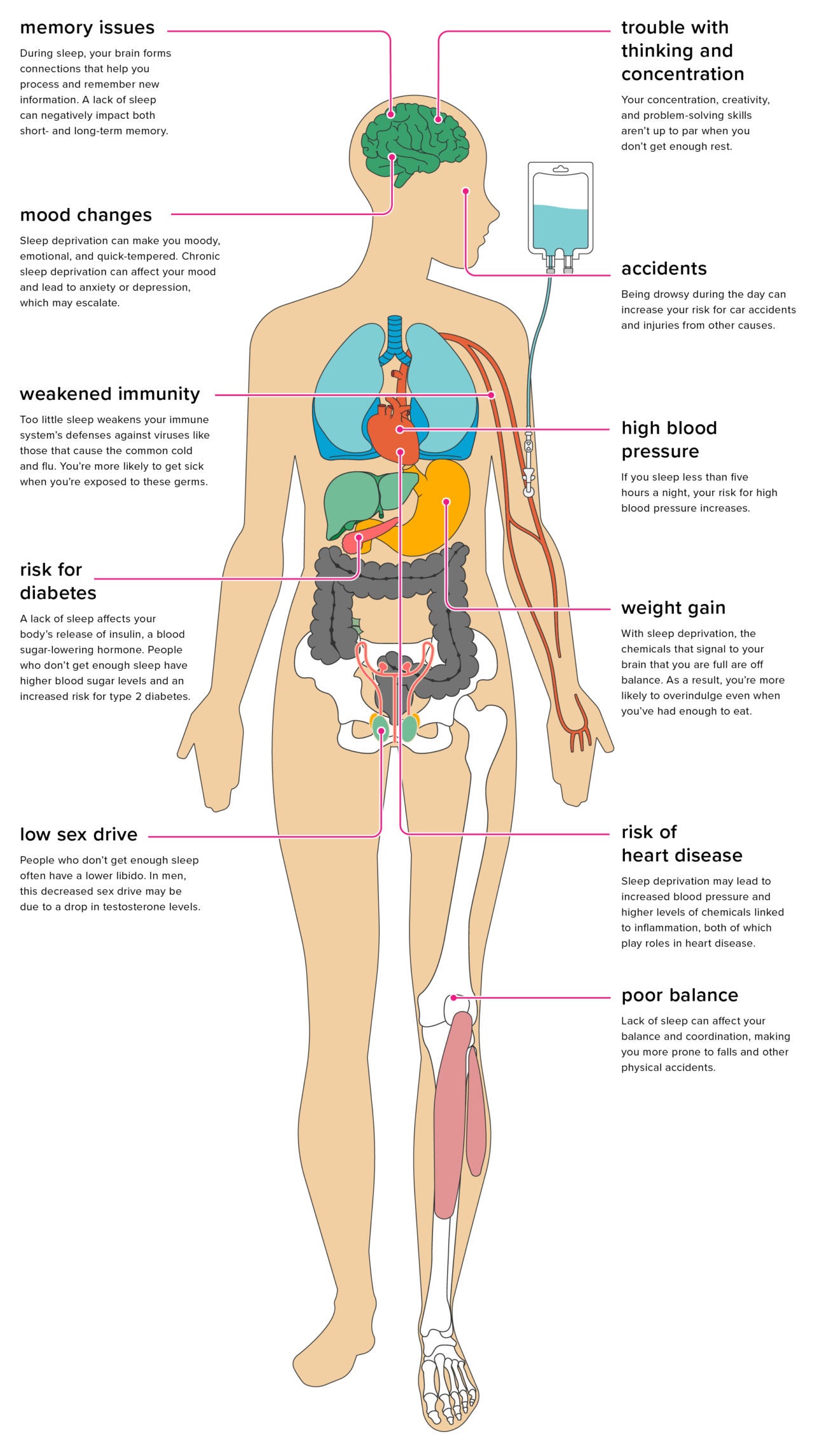
Cognitive Decline
Sleep deprivation also affects cognitive abilities. Memory, focus, and decision-making skills suffer.
Key cognitive impacts include:
- Memory Issues: Poor sleep affects memory retention.
- Lack of Focus: Sleep-deprived people struggle to concentrate.
- Decision-Making: Judgement gets impaired with less sleep.
These cognitive issues can affect daily life and productivity.
Credit: www.healthline.com
Physical Health Consequences
Sleep deprivation has numerous physical health consequences. Neglecting sleep affects different parts of the body. This can lead to serious health issues. Here, we will discuss two major concerns: heart disease and obesity.
Heart Disease
Not getting enough sleep can hurt your heart. People who sleep less are more likely to get heart disease. This is because sleep helps control blood pressure. High blood pressure can damage your heart and blood vessels. Poor sleep also increases stress, leading to heart problems.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Heart |
|---|---|
| High Blood Pressure | Damages arteries, leading to heart attacks. |
| Stress Hormones | Increases risk of heart disease. |
Obesity
Sleep deprivation also links to obesity. Lack of sleep affects hormones that control hunger. When you are tired, you crave high-calorie foods. This leads to weight gain.
- Ghrelin: This hormone makes you feel hungry. Lack of sleep increases ghrelin levels.
- Leptin: This hormone makes you feel full. Lack of sleep decreases leptin levels.
These changes cause you to eat more. This leads to weight gain and obesity. Obesity then leads to other health problems like diabetes and joint pain.
Immune System Impairment
Sleep deprivation can severely impact your health. One significant effect is on the immune system. Without enough sleep, your immune system becomes weak and less effective. This increases your risk of various health issues.
Increased Infections
When you don’t get enough sleep, your body struggles to fight off infections. This happens because sleep helps your immune system produce protective proteins called cytokines. These proteins help fight infections and inflammation.
A lack of sleep reduces the production of cytokines. This makes you more susceptible to common illnesses like the flu and cold. According to studies, people who sleep less than seven hours a night are three times more likely to catch a cold compared to those who sleep eight or more hours.
Here are some common infections linked to sleep deprivation:
- Common cold
- Flu
- Respiratory infections
Inflammation
Sleep deprivation also leads to increased inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is a risk factor for many serious health conditions, including heart disease and diabetes.
Studies show that even a single night of poor sleep can cause an immediate inflammatory response. This response includes an increase in inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP).
The table below summarizes the effects of inflammation due to sleep deprivation:
| Health Condition | Associated Inflammation Marker |
|---|---|
| Heart Disease | C-reactive Protein (CRP) |
| Diabetes | Interleukin-6 (IL-6) |
| Arthritis | Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) |
Managing your sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night. This helps your body stay strong and fight off infections effectively.
Credit: wellbeing.jhu.edu
Impact On Daily Performance
Sleep deprivation can significantly affect our daily performance. Let’s explore how lack of sleep impacts work efficiency and accident risk.
Work Efficiency
Lack of sleep reduces work efficiency. You find it hard to focus on tasks. Simple activities take longer to complete. Memory and decision-making skills suffer.
Sleep-deprived employees make more errors. They often need more breaks. This leads to lower productivity. Teams also suffer as collaboration becomes challenging.
Consider this comparison:
| Well-rested | Sleep-deprived |
|---|---|
| High focus | Poor concentration |
| Fast task completion | Slow task completion |
| Few errors | Many errors |
| Good memory | Poor memory |
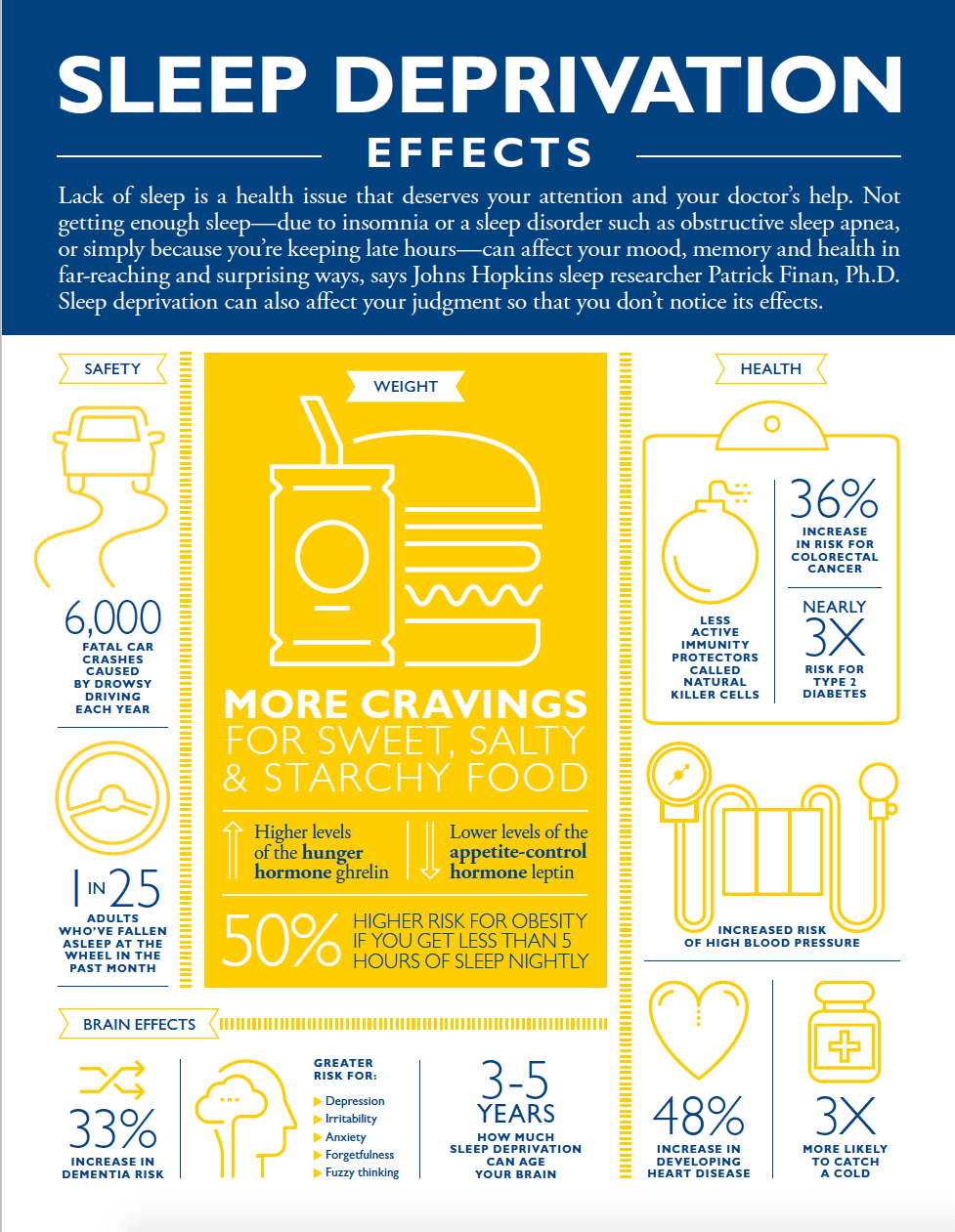
Accident Risk
Sleep deprivation increases accident risk. Tiredness leads to slower reaction times. It becomes hard to stay alert. The risk of car crashes rises significantly.
In workplaces, sleep-deprived workers face more injuries. They struggle with equipment and tools. Here are some statistics:
- Sleepy drivers cause 1 in 5 car accidents.
- Fatigued workers have a 70% higher risk of injury.
Ensuring adequate sleep can save lives. It improves overall safety for everyone.
Sleep Deprivation In Children
Children need more sleep than adults. Lack of sleep can harm their health. It affects their growth, learning, and mood.
Developmental Issues
Sleep deprivation can lead to developmental issues in children. Proper sleep is crucial for brain development. Without enough sleep, their brain can’t grow well.
Sleep is also important for physical growth. Growth hormones are released during sleep. Lack of sleep means fewer growth hormones.
Children may also have weakened immune systems. They might fall sick more often. Good sleep helps keep their body strong.
Academic Performance
Sleep deprivation affects academic performance. Tired children can’t focus well in class. They may struggle to understand lessons.
Children need sleep to store new information. Lack of sleep can lead to poor memory. They might forget what they learned in school.
Sleep-deprived children may also have trouble with:
- Completing homework
- Participating in class activities
- Taking tests
Good sleep helps children stay alert. It makes learning easier and more fun.
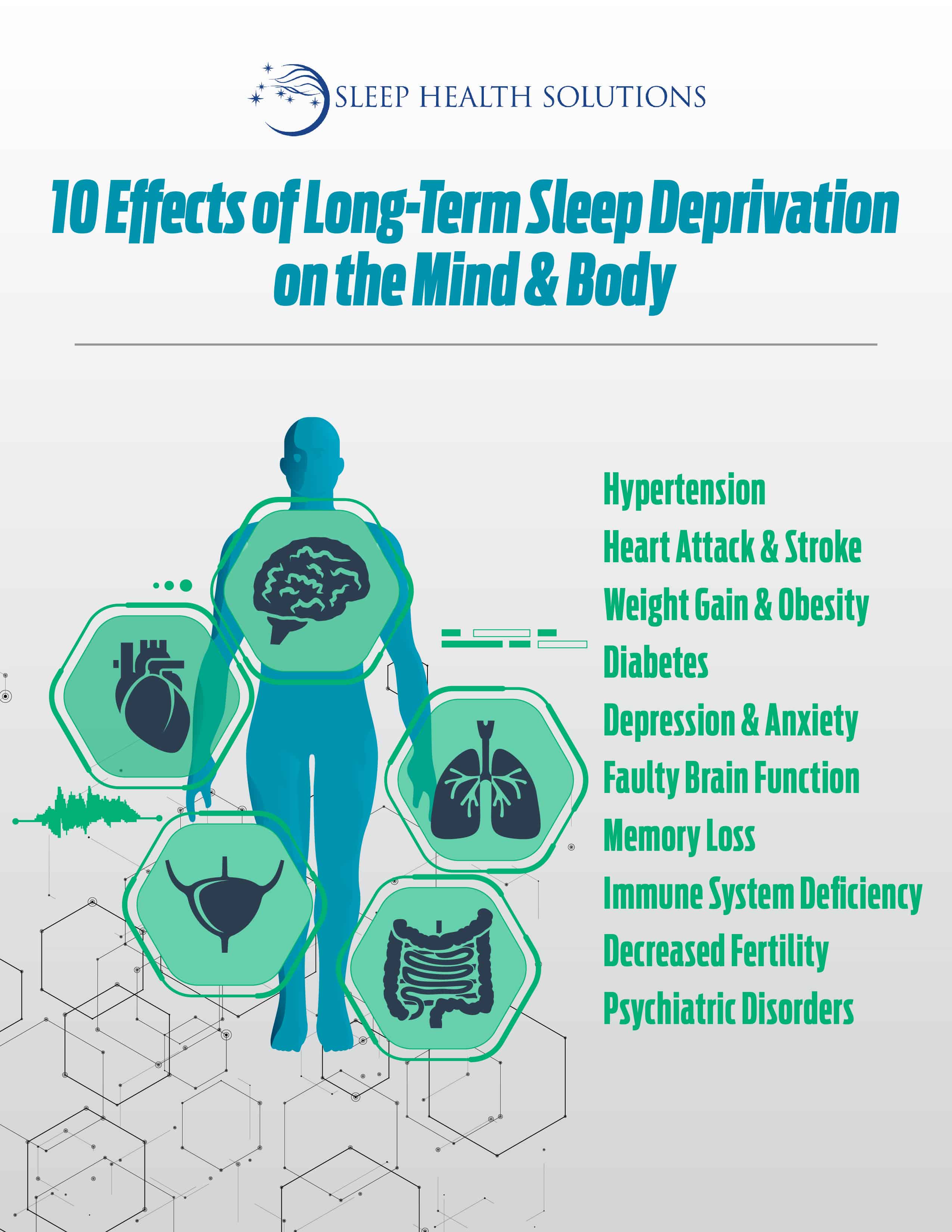
Credit: www.sleephealthsolutionsohio.com
Long-term Health Risks
Sleep deprivation does more harm than just making you tired. It has serious effects on your health. Missing out on sleep can lead to many long-term health risks. Below, we explore some of these risks in detail.
Chronic Diseases
Lack of sleep can lead to chronic diseases. These include:
- Heart Disease: Sleep deprivation increases the risk of heart problems. Your heart needs rest to stay healthy.
- Diabetes: Poor sleep can affect your blood sugar levels. This increases the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Obesity: Lack of sleep affects your hunger hormones. This can lead to weight gain and obesity.
- High Blood Pressure: Not getting enough sleep can raise your blood pressure. This is bad for your heart and blood vessels.
Life Expectancy
Poor sleep can shorten your life. Studies show that people who sleep less live shorter lives. Sleep helps your body repair and stay healthy. Without enough sleep, your body ages faster.
Consider this table showing the effects of sleep on life expectancy:
| Hours of Sleep | Average Life Expectancy |
|---|---|
| Less than 5 hours | 65 years |
| 5-6 hours | 70 years |
| 7-8 hours | 75 years |
| More than 8 hours | 72 years |
These numbers show the importance of sleep. Getting the right amount of sleep can help you live longer.
Coping Mechanisms
Sleep deprivation affects your health in many ways. Coping mechanisms can help. These strategies can improve your sleep and well-being. Let’s explore some effective coping mechanisms.
Sleep Hygiene
Good sleep hygiene is essential for quality rest. Follow these tips to improve it:
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule. Go to bed and wake up at the same time daily.
- Create a bedtime routine. Engage in relaxing activities before sleep.
- Keep your bedroom dark and quiet. Use blackout curtains or earplugs if needed.
- Limit screen time before bed. The blue light can disrupt your sleep cycle.
- Avoid caffeine and heavy meals before bedtime. They can make falling asleep difficult.
Stress Management
Managing stress is crucial for better sleep. Here are some techniques:
- Exercise regularly. Physical activity can reduce stress levels.
- Practice mindfulness. Meditation and yoga can calm your mind.
- Stay organized. Planning your tasks can minimize stress.
- Talk about your feelings. Sharing with friends can relieve stress.
- Engage in hobbies. Doing what you love can help you unwind.
Both sleep hygiene and stress management are key coping mechanisms. Incorporate these strategies into your daily routine for better health.
Seeking Professional Help
Sleep deprivation affects our health in many ways. Sometimes, simple lifestyle changes aren’t enough. In such cases, seeking professional help becomes crucial. Professionals can offer tailored solutions to improve sleep quality. Below are two main ways professionals can assist.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions are often needed for severe sleep deprivation. Doctors can prescribe medications to help you sleep better. These medications are called sleep aids. They help you fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer. Always use these drugs under a doctor’s supervision.
Doctors might also check for underlying health issues. Conditions like sleep apnea or insomnia often cause sleep deprivation. Treating these conditions can improve sleep quality. Sometimes, doctors may recommend supplements. These can include melatonin or magnesium. These supplements can help regulate your sleep cycle.
Therapies
Therapies offer a non-medical approach to tackle sleep issues. One common therapy is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I). This therapy helps change negative thoughts about sleep. It also teaches relaxation techniques to improve sleep quality.
Light therapy is another option. It involves exposure to bright light at specific times. This helps reset your internal clock. Therapists might also suggest sleep hygiene education. This includes tips for a better sleep environment. For example:
- Keeping the bedroom dark and cool
- Limiting screen time before bed
- Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule
Combining these methods can lead to better sleep and improved health.
Conclusion
Sleep deprivation can severely impact your health. Prioritize good sleep to improve mental and physical well-being. Consistent rest boosts immune function and mood. Make sleep a crucial part of your health routine. Your body and mind will thank you for the rejuvenating benefits of quality sleep.