The Science Behind Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. It can boost metabolism and improve overall health.
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity due to its potential health benefits. This eating pattern involves alternating between eating and fasting periods. Research suggests intermittent fasting can boost metabolism, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote weight loss. It may also enhance brain function and reduce inflammation.
The simplicity and flexibility of intermittent fasting make it accessible for many people. Whether you follow the 16/8 method, the 5:2 diet, or another variation, intermittent fasting can fit various lifestyles. By focusing on when you eat rather than what you eat, intermittent fasting offers a sustainable approach to improving health and well-being.
Introduction To Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained popularity in recent years. It involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. People use it to improve health and lose weight. Let’s explore what intermittent fasting is and its history.
What Is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern. It focuses on when to eat, not what to eat. There are different methods of fasting:
- 16/8 method: Fast for 16 hours, eat during 8 hours.
- 5:2 diet: Eat normally for 5 days, fast for 2 days.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: Fast for 24 hours once or twice a week.
During fasting periods, only drink water, coffee, or tea. Fasting helps the body to use stored fat for energy.
Brief History
Fasting is not new. It dates back to ancient times. Early humans fasted naturally due to food scarcity. Many religions also practice fasting:
- Islam: Ramadan involves fasting from dawn to sunset.
- Christianity: Lent includes periods of fasting.
- Buddhism: Some monks fast daily from noon to dawn.
Modern science has shown that fasting has health benefits. It can improve metabolism and brain function.
Intermittent fasting is a simple way to eat less and stay healthy.

Credit: www.lifescapepremier.com
Types Of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity for its health benefits. There are several types of intermittent fasting, each with its unique approach. Understanding these methods can help you choose the best one for your lifestyle and goals.
16/8 Method
The 16/8 Method involves fasting for 16 hours each day. You eat all your meals within an 8-hour window. This method is simple to follow and fits into most daily routines.
For example, you might eat between 12 PM and 8 PM. Outside this window, you only drink water, coffee, or tea without sugar.
5:2 Diet
The 5:2 Diet is another popular method. You eat normally for five days a week. On the other two days, you restrict your calorie intake to about 500-600 calories.
This diet is flexible and allows you to choose which days to fast. It is great for those who prefer not to fast daily.
Eat-stop-eat
The Eat-Stop-Eat method involves fasting for 24 hours once or twice a week. For example, you might fast from dinner one day to dinner the next day.
This method can be challenging for beginners. Yet, it offers significant health benefits and promotes weight loss.
How Intermittent Fasting Works
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity for its potential health benefits. But how does it work? Let’s dive into the science behind it.
Metabolic Processes
During intermittent fasting, the body undergoes several metabolic processes. When you fast, your body switches from burning glucose to burning fat. This process is known as ketosis. In ketosis, the liver converts fat into ketones, which serve as an energy source.
Another important process is autophagy. Autophagy is the body’s way of cleaning out damaged cells. It helps regenerate newer, healthier cells. This process is crucial for maintaining cellular health and longevity.
| Metabolic Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Ketosis | Switch from burning glucose to burning fat |
| Autophagy | Cleaning out damaged cells for regeneration |
Hormonal Changes
Intermittent fasting triggers several hormonal changes in the body. One of the key hormones affected is insulin. Fasting helps lower insulin levels. Lower insulin levels make it easier for the body to access stored fat for energy.
Another important hormone is human growth hormone (HGH). Fasting can increase HGH levels. Higher HGH levels aid in fat loss and muscle gain. This hormone is crucial for overall growth and metabolism.
- Insulin – Lower levels help access stored fat
- Human Growth Hormone (HGH) – Higher levels aid in fat loss and muscle gain
Credit: rhealthc.com
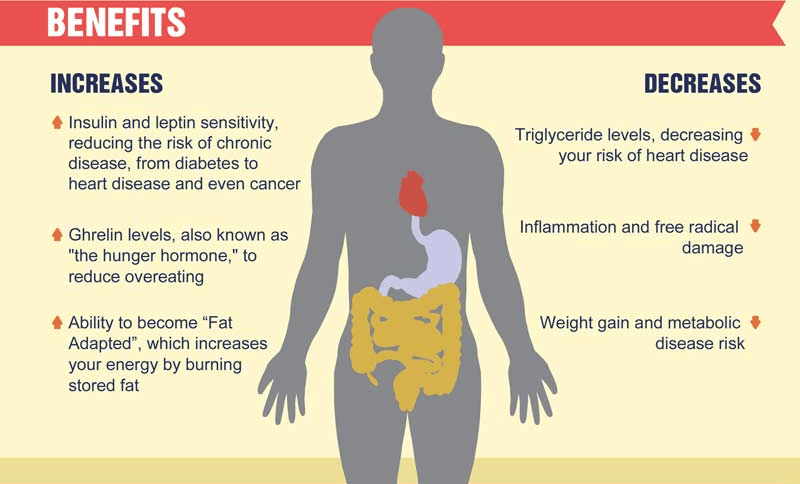
Health Benefits
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity for its numerous health benefits. It isn’t just a trend but is backed by science. Let’s explore the most important health advantages of intermittent fasting.
Weight Loss
Intermittent fasting can help with weight loss. It does this by reducing calorie intake. When you eat fewer meals, you consume fewer calories. This can lead to a caloric deficit, which is essential for weight loss.
Studies show that intermittent fasting boosts metabolism. This helps your body burn more calories throughout the day. Fasting also lowers insulin levels, which helps your body use stored fat for energy.
- Reduces calorie intake
- Boosts metabolism
- Lowers insulin levels
Improved Metabolic Health
Intermittent fasting can improve metabolic health. It does this by regulating blood sugar levels and reducing insulin resistance. This is crucial for preventing Type 2 diabetes.
Fasting also reduces inflammation, which is linked to many chronic diseases. It helps in lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
| Health Metric | Effect |
|---|---|
| Blood Sugar Levels | Regulated |
| Insulin Resistance | Reduced |
| Inflammation | Lowered |
| Blood Pressure | Reduced |
| Cholesterol Levels | Lowered |
Longevity
Intermittent fasting may help you live longer. Studies on animals show that fasting can extend lifespan. Scientists believe this might be true for humans as well.
Fasting triggers cellular repair processes like autophagy. This helps remove damaged cells and promotes the growth of new, healthy cells. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, fasting can slow down aging.
- May extend lifespan
- Triggers cellular repair
- Removes damaged cells
- Promotes growth of new cells
- Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress
These health benefits make intermittent fasting a powerful tool. It can improve your life in many ways.
Potential Risks
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity for its health benefits. But it also has potential risks. Understanding these risks is crucial before starting any fasting regimen. This section explores the possible downsides of intermittent fasting.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Intermittent fasting limits the eating window. This can make it hard to get all necessary nutrients. Vitamins and minerals are essential for the body. Missing out on these can lead to deficiencies.
Here is a table showing common deficiencies and their symptoms:
| Nutrient | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Vitamin D | Weak bones, fatigue |
| Iron | Anemia, weakness |
| Calcium | Brittle nails, poor bone health |
To avoid deficiencies, eat a balanced diet. Fruits, vegetables, and proteins are crucial. Supplements can also help.
Impact On Mental Health
Intermittent fasting can affect your mental health. Some people may experience mood swings and irritability. This is due to changes in blood sugar levels.
Here are some common mental health issues related to fasting:
- Increased stress
- Feeling anxious
- Depression symptoms
To minimize mental health risks, monitor your mood. Make sure to stay hydrated. Consult a healthcare professional if you experience severe symptoms.
Scientific Studies
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity for its health benefits. Scientists have explored its effects through various studies. Below, we break down some key research findings and ongoing studies.
Key Research Findings
Several studies highlight the benefits of intermittent fasting. Here are some key findings:
- Weight Loss: Research shows intermittent fasting helps in weight loss.
- Improved Metabolism: Studies indicate an increase in metabolic rate.
- Longevity: Fasting may extend lifespan according to animal studies.
- Reduced Inflammation: Regular fasting helps reduce inflammation markers.
Researchers found intermittent fasting can lower blood sugar levels. It also improves insulin sensitivity. This helps in managing diabetes. Furthermore, studies show fasting enhances brain function. It may protect against neurodegenerative diseases.
Ongoing Studies
Ongoing research aims to uncover more benefits of intermittent fasting. Current studies focus on:
- Cancer Prevention: Scientists are studying fasting’s impact on cancer cells.
- Heart Health: Researchers are exploring how fasting affects heart disease risk.
- Gut Health: Studies investigate the effects of fasting on gut microbiome.
- Mental Health: Ongoing research looks at fasting’s impact on mood disorders.
These studies are crucial for understanding intermittent fasting’s full potential. They aim to provide more evidence-based guidelines for health improvements.
Practical Tips
Intermittent fasting is popular for its health benefits. Many people find it hard to start and stay consistent. Below are practical tips to help you on your journey.
Getting Started
Starting intermittent fasting can be simple.
- Choose a fasting schedule: Pick a plan that fits your lifestyle. Common plans include the 16/8 method and the 5:2 diet.
- Start gradually: Ease into it. Begin with shorter fasting periods and increase over time.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water. Herbal teas and black coffee are also good choices.
- Eat balanced meals: Focus on nutrient-dense foods during eating windows. Include proteins, healthy fats, and vegetables.
- Listen to your body: If you feel dizzy or weak, adjust your plan.
Staying Consistent
Consistency is key to successful intermittent fasting.
- Plan your meals: Plan your meals ahead of time. Th

Credit: www.soonfasting.com
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting offers numerous health benefits supported by scientific research. It can improve metabolism and support weight management. This approach is simple yet effective, making it popular. Consider trying intermittent fasting to enhance your overall health. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new dietary regimen.
Your body will thank you.






