The Science of Neuroplasticity And Learning
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. Learning alters these connections, enhancing cognitive skills.
Neuroplasticity allows our brains to adapt and change throughout our lives. This dynamic process is fundamental to learning and memory. Whenever we acquire new skills or knowledge, our brain’s neural networks rewire themselves. This adaptability helps in recovering from brain injuries and improving mental functions.
Understanding neuroplasticity can revolutionize education, therapy, and personal development. With targeted exercises and practices, we can enhance our cognitive abilities and mental health. The science of neuroplasticity underscores the importance of continuous learning and mental agility. Embracing these concepts can lead to better educational outcomes and overall well-being.

Credit: www.linkedin.com
Introduction To Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to change and adapt. This is essential for learning and memory. Let’s explore its definition, importance, and history.
Definition And Importance
Neuroplasticity means the brain can rewire itself. This happens through new experiences and learning. It allows the brain to form new connections. This ability helps in recovering from injuries. It also aids in acquiring new skills.
Neuroplasticity is crucial for cognitive development. It supports lifelong learning. It helps with adapting to new environments. Neuroplasticity also plays a role in emotional regulation.
Historical Background
Scientists once believed the brain was static. They thought it could not change after childhood. This belief persisted for centuries.
In the 20th century, research showed the brain’s ability to adapt. Studies on animals and humans provided evidence. This changed our understanding of the brain.
Modern research continues to uncover the brain’s plasticity. These discoveries have transformed neuroscience. They have also impacted education and therapy.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Neuroplasticity | The brain’s ability to reorganize itself. |
| Cognitive Development | The process of learning and acquiring knowledge. |
- Neuroplasticity helps in memory formation.
- It aids in learning new languages.
- It supports recovery from brain injuries.
Credit: biotech.ucdavis.edu
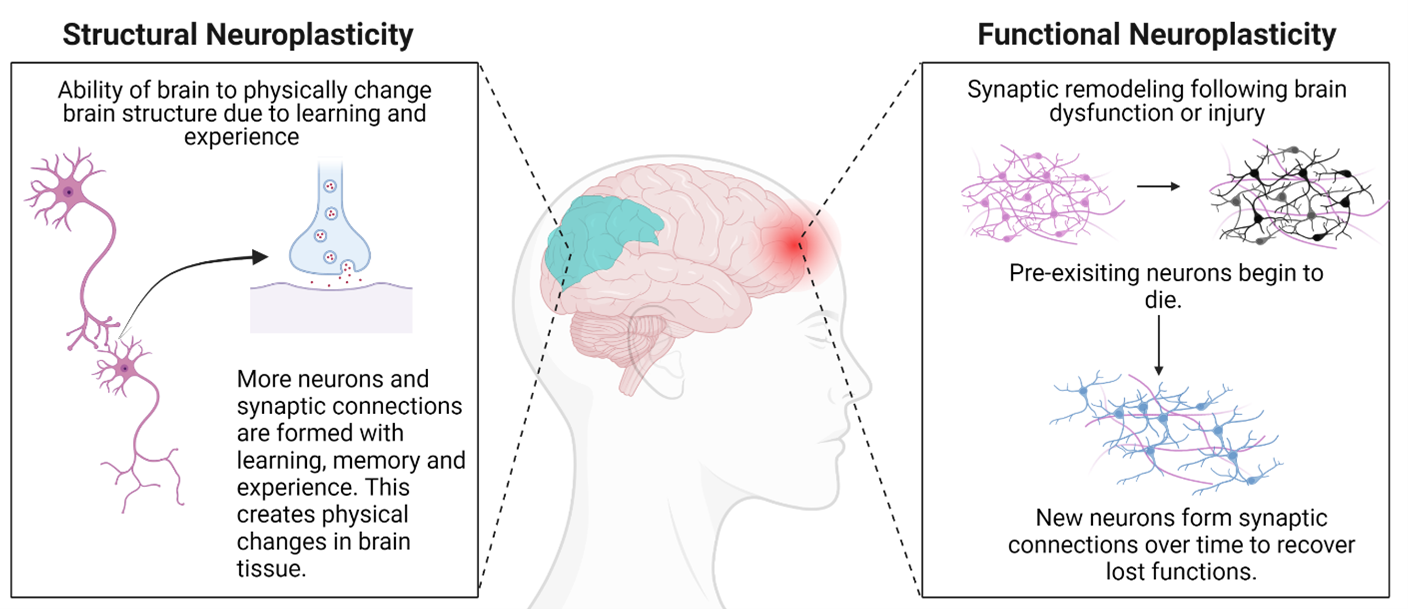
Mechanisms Of Neuroplasticity
The science of neuroplasticity reveals how our brain can change. This ability helps us learn and adapt. These changes happen through various mechanisms of neuroplasticity. Let’s explore two key types: synaptic plasticity and structural plasticity.
Synaptic Plasticity
Synaptic plasticity involves changes in the strength of connections between neurons. These connections are called synapses. When we learn, synapses become stronger or weaker. This process is known as long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD).
Here are some key points about synaptic plasticity:
- Neurons communicate through electrical signals.
- Repeated use of a synapse strengthens it (LTP).
- Lack of use can weaken a synapse (LTD).
- Strong synapses improve memory and learning.
Imagine synaptic plasticity as a path in the forest. The more you walk, the clearer it becomes. This helps you remember and learn better.
Structural Plasticity
Structural plasticity refers to changes in the brain’s physical structure. This can include the growth of new neurons and connections. These changes are more visible over time.
Here are some key points about structural plasticity:
- New neurons can grow in certain brain areas.
- Connections between neurons can increase or decrease.
- Learning new skills can lead to structural changes.
- Physical activity can promote brain growth.
Think of structural plasticity as remodeling a house. You can add new rooms or strengthen walls. This helps the brain adapt and improve over time.
| Type of Plasticity | Key Features | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Synaptic Plasticity | Changes in synapse strength | Learning new facts, remembering names |
| Structural Plasticity | Changes in brain structure | Learning to play an instrument, physical exercise |
Neuroplasticity Across The Lifespan
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to change and adapt. This happens throughout life. The brain can rewire itself, forming new neural connections. This ability supports learning and memory. Let’s explore how neuroplasticity works at different life stages.
Childhood Brain Development
In childhood, the brain is very flexible. It can easily form new connections. Kids learn new skills quickly. This is due to high neuroplasticity. The brain grows rapidly, making it easier to learn languages, math, and social skills.
During this stage, experiences shape the brain significantly. Positive experiences like reading and playing help brain growth. Negative experiences can hinder development. Early childhood education is crucial for brain development.
Adult Brain Changes
Neuroplasticity continues in adulthood, though it slows down. Adults can still learn new skills and adapt. Engaging in activities like learning a new language or playing an instrument boosts neuroplasticity. These activities create new brain pathways.
Adults benefit from mental and physical exercises. Regular exercise improves brain health. Mental challenges like puzzles keep the brain sharp. Social interactions also enhance brain function. Continuous learning keeps the brain agile.
| Life Stage | Neuroplasticity Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Childhood | High neuroplasticity, rapid brain growth, easy learning |
| Adulthood | Slower neuroplasticity, benefits from mental and physical activities |
- Neuroplasticity allows the brain to adapt and change.
- Childhood is a crucial period for brain development.
- Adults can still enhance brain function through various activities.
Understanding neuroplasticity helps us appreciate the brain’s adaptability. It encourages us to engage in activities that boost brain health.
Role In Learning And Memory
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to change and adapt. This process plays a crucial role in learning and memory. Understanding how neuroplasticity works can help unlock the secrets of cognitive processes and memory formation.
Cognitive Processes
Cognitive processes involve how we think and understand the world. These processes include attention, perception, and problem-solving. Neuroplasticity enhances these cognitive functions by creating new neural pathways. This makes learning new skills easier and faster.
Let’s break down the cognitive processes affected by neuroplasticity:
- Attention: Helps focus on important information.
- Perception: Enhances how we interpret sensory data.
- Problem-solving: Boosts our ability to find solutions.
Memory Formation
Memory formation is another key area influenced by neuroplasticity. The brain forms memories by creating new connections between neurons. Stronger connections lead to better memory retention.
Here’s a simple table to explain memory formation stages:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Encoding | Information enters the brain. |
| Storage | Information is stored for future use. |
| Retrieval | Stored information is accessed. |
Neuroplasticity strengthens these stages, making it easier to learn and remember. Activities like reading and puzzles can boost brain plasticity. This makes learning more effective and enjoyable.
Factors Influencing Neuroplasticity
The science of neuroplasticity reveals the brain’s ability to change and adapt. Various factors influence how effectively our brains can rewire themselves. This section explores two key factors: environmental stimuli and genetic factors.
Environmental Stimuli
Environmental stimuli play a significant role in neuroplasticity. Our surroundings impact how our brains develop and adapt. Different forms of stimuli can include:
- Physical Exercise: Regular physical activity boosts brain health.
- Social Interactions: Engaging with others enhances cognitive functions.
- Cognitive Activities: Puzzles, reading, and learning new skills stimulate brain growth.
A stimulating environment encourages the brain to form new connections. The richer the environment, the more adaptable the brain becomes. Children exposed to diverse experiences tend to have more robust neural networks.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors also influence neuroplasticity. Our genes provide a blueprint for brain development. Key genetic elements include:
- BDNF Gene: This gene supports neuron growth and survival.
- COMT Gene: It affects dopamine levels, influencing learning and memory.
- APOE Gene: Linked to cognitive performance and brain health.
While genetics set the stage, they interact with environmental stimuli. A supportive environment can enhance genetic potential, leading to better neuroplasticity outcomes.
| Factor | Influence on Neuroplasticity |
|---|---|
| Environmental Stimuli | Boosts brain adaptability and cognitive functions |
| Genetic Factors | Provides a blueprint for brain development |
Understanding these factors helps us create environments that support brain health and learning. Both environmental stimuli and genetic factors are crucial in shaping our brain’s ability to adapt and grow.
Techniques To Enhance Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to adapt and change. By understanding techniques to enhance neuroplasticity, we can improve our learning and cognitive functions. This section covers effective methods to boost neuroplasticity, including physical exercise and mental stimulation.
Physical Exercise
Physical exercise is crucial for brain health. It increases blood flow to the brain, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen. Exercise also releases hormones that promote the growth of new brain cells.
- Aerobic exercises like running, swimming, and cycling are highly beneficial.
- Engaging in strength training can also boost cognitive function.
- Even simple activities such as walking or dancing can help.
Incorporating regular exercise into your routine can significantly enhance neuroplasticity.
Mental Stimulation
Mental stimulation involves challenging your brain with new and complex tasks. This can foster the development of new neural pathways.
- Learning a new language or musical instrument can be highly effective.
- Engaging in puzzles like Sudoku or crosswords stimulates the brain.
- Reading books, especially on diverse topics, keeps the brain active.
These activities encourage the brain to form new connections, enhancing neuroplasticity.
Combining physical exercise and mental stimulation can lead to optimal brain health. These techniques are simple yet powerful ways to boost your cognitive abilities.
Applications In Education
The science of neuroplasticity has revolutionized our understanding of the brain. This new knowledge has significant implications for education. Teachers can now use strategies that foster brain growth and adaptability. These applications in education are transforming how students learn and retain information.
Teaching Strategies
Effective teaching strategies leverage the brain’s ability to change. Teachers can use various techniques to enhance learning:
- Active Learning: Engage students in hands-on activities to strengthen neural connections.
- Spaced Repetition: Review material at intervals to improve long-term retention.
- Multi-Sensory Learning: Use visual, auditory, and kinesthetic methods to cater to different learning styles.
These strategies help create a stimulating learning environment. They encourage students to build stronger neural pathways.
Learning Interventions
Learning interventions are specific actions to support struggling students. These interventions are designed based on neuroplasticity principles:
| Intervention | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Targeted Skill Practice | Focus on specific skills to strengthen weak areas. |
| Cognitive Training | Use exercises that improve memory and attention. |
| Personalized Learning Plans | Create tailored plans to meet individual student needs. |
These interventions can help students achieve their full potential. They ensure that each child receives the support they need.
Future Directions
The study of neuroplasticity and learning has opened up exciting future directions. Researchers are exploring new avenues to harness the brain’s ability to change and adapt. These new directions hold promise for treatments and educational methods. Below, we delve into potential therapies and research challenges.
Potential Therapies
Neuroplasticity offers hope for treating various conditions. Scientists are developing therapies that leverage the brain’s adaptability. These therapies could help with:
- Stroke recovery: Enhancing brain function after a stroke.
- Traumatic brain injury: Aiding in the healing process.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Slowing down conditions like Alzheimer’s.
Innovative techniques include:
- Brain stimulation: Using electrical impulses to encourage brain activity.
- Virtual reality: Simulating environments for cognitive rehabilitation.
- Neurofeedback: Training the brain to self-regulate.
Research Challenges
Despite the exciting prospects, researchers face significant challenges. Understanding the full complexity of neuroplasticity is difficult. Key challenges include:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Individual variability | Different brains respond differently to treatments. |
| Long-term effects | Ensuring therapies have lasting positive impacts. |
| Ethical considerations | Balancing treatment benefits with potential risks. |
Researchers continue to push boundaries despite these challenges. The future of neuroplasticity research holds immense promise.

Credit: solportal.ibe-unesco.org
Conclusion
Understanding neuroplasticity can transform how we approach learning. This science reveals our brain’s incredible ability to adapt. Embracing these insights can enhance educational methods and personal growth. Stay curious, and leverage neuroplasticity for continuous improvement. Unlock your brain’s potential and make lifelong learning a rewarding journey.






