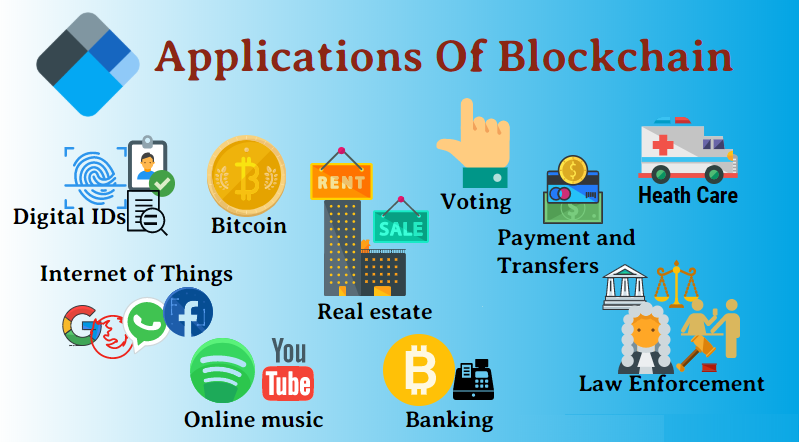
Understanding Blockchain Technology And Its Applications
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It ensures transparency, security, and immutability.
Blockchain has revolutionized various industries by providing a secure and transparent way to record transactions. Originally developed for Bitcoin, blockchain’s potential extends beyond cryptocurrencies. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Industries such as finance, healthcare, supply chain, and real estate benefit from blockchain applications.
Smart contracts, which execute automatically when conditions are met, further enhance blockchain’s versatility. The technology’s ability to prevent fraud and ensure data integrity makes it invaluable. As blockchain continues to evolve, its applications will likely expand, offering innovative solutions to complex problems.
Introduction To Blockchain
Blockchain technology is changing many industries. It offers secure and transparent transactions. Understanding its basics can help you see its potential. This section introduces blockchain and its key elements.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a digital ledger. It records transactions across many computers. These records are secure and hard to change. Each block in the chain holds many transactions. Once a block is full, it links to the previous block.
The chain of blocks forms a secure and transparent record. This record is open for anyone to see but difficult to alter. This makes blockchain trustworthy and reliable.
History And Evolution
Blockchain started with Bitcoin in 2008. Satoshi Nakamoto, an unknown person, introduced it. The first blockchain was a part of the Bitcoin system. Bitcoin used blockchain to record all transactions.
In 2015, Ethereum brought new features. It introduced smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts with the agreement terms directly written into code. This expanded blockchain’s uses beyond cryptocurrencies.
Today, blockchain is evolving fast. It is used in finance, healthcare, supply chains, and more. Many new blockchains are being developed with unique features.

Credit: www.simplilearn.com
How Blockchain Works
Blockchain technology might sound complex, but it is quite simple. It consists of blocks, each containing data, linked together. This creates a chain of blocks, hence the name “blockchain”. Each block is immutable, meaning it cannot be changed. This ensures the data’s integrity.
Key Components
The main components of blockchain are:
- Blocks: Each block stores data. This could be transactions or records.
- Chains: Blocks are linked together in a chain. This keeps the data secure.
- Nodes: Computers in the network. Each node has a copy of the blockchain.
- Miners: Special nodes that validate transactions and add new blocks.
- Cryptography: Ensures data is secure and only accessible to the intended users.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms ensure all nodes agree on the blockchain state. Two common mechanisms are:
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Proof of Work (PoW): | Miners solve complex puzzles. The first to solve adds a new block. |
| Proof of Stake (PoS): | Validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold. |
Both methods ensure the blockchain remains secure and decentralized.
Types Of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is not just one type. It has various forms, each serving a different purpose. Understanding these types can help you choose the right one for your needs. Below, we explore the three main types of blockchains: Public, Private, and Consortium.
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are open for anyone to join. They are decentralized and transparent. Everyone can see all transactions. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum. Public blockchains use a consensus algorithm. This ensures that no single entity controls the network. They are secure but can be slow and expensive.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are restricted. Only selected individuals can join. These are often used by businesses. They offer more privacy than public blockchains. A single entity controls the network. This makes them faster and cheaper. But they are less secure. Examples include Hyperledger and Ripple.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains are semi-decentralized. A group of organizations manages them. They offer a middle ground. They are more secure than private blockchains. They are also more efficient than public blockchains. Examples include R3 and Quorum. These blockchains are often used in finance and supply chain management.
Blockchain Security
Blockchain security is critical for the success of the technology. It ensures the safety and reliability of transactions and data. Understanding the core elements of blockchain security is essential for grasping its potential.
Cryptography
Cryptography plays a vital role in blockchain security. It uses complex mathematical algorithms to secure data. Every transaction is encrypted, making it nearly impossible to hack.
There are two main types of cryptography in blockchain:
- Symmetric-key cryptography: Uses the same key for encryption and decryption.
- Asymmetric-key cryptography: Uses a pair of keys, one public and one private.
Asymmetric-key cryptography is widely used in blockchain. The public key is visible to everyone, while the private key remains confidential. This ensures that only the rightful owner can access their data.
Decentralization
Decentralization is another cornerstone of blockchain security. It eliminates the need for a central authority. Instead, the network consists of multiple nodes, each holding a copy of the blockchain.
Key benefits of decentralization include:
- Redundancy: Data is replicated across multiple nodes, ensuring no single point of failure.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to every participant in the network.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted.
Decentralization makes the blockchain resistant to attacks. Hackers would need to compromise more than half of the nodes to alter the data. This is known as a 51% attack and is highly unlikely.
| Security Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Cryptography | Secures data and transactions |
| Decentralization | Eliminates single points of failure |
| Transparency | All transactions are visible |
| Immutability | Data cannot be altered once recorded |
Combining cryptography and decentralization, blockchain offers robust security. This makes it a reliable technology for various applications.
Blockchain In Finance
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the financial industry. It offers secure and transparent solutions. It reduces fraud and increases efficiency. Blockchain provides a decentralized system for financial transactions. This section explores the applications of blockchain in finance.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies that use blockchain technology. Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency. Now, there are many others like Ethereum and Ripple.
- Decentralization: No central authority controls cryptocurrencies.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger.
- Security: Transactions are secure and encrypted.
People use cryptocurrencies for various reasons. Some invest in them. Others use them for online purchases. Businesses also accept them as payment.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts. They use blockchain to enforce terms automatically.
- Efficiency: Smart contracts reduce the need for intermediaries.
- Automation: They execute automatically when conditions are met.
- Cost-Effective: They lower transaction costs significantly.
Smart contracts have many applications in finance. They automate loan approvals. They streamline insurance claims. They ensure compliance with regulations.
| Feature | Cryptocurrencies | Smart Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Decentralization | Yes | Yes |
| Transparency | Yes | Yes |
| Security | High | High |
| Automation | No | Yes |
| Cost-Effective | Yes | Yes |
The financial industry is rapidly adopting blockchain. Cryptocurrencies and smart contracts are leading the way. They offer secure, efficient, and cost-effective solutions.

Credit: amt-lab.org
Blockchain Beyond Finance
Blockchain technology is often associated with cryptocurrencies and financial transactions. But its potential goes far beyond finance. This technology can transform various sectors, bringing efficiency, security, and transparency. Let’s explore how blockchain is revolutionizing areas outside finance.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can enhance supply chain management by providing real-time tracking of goods. Companies can trace products from origin to destination. This transparency ensures product authenticity and quality. It also helps in reducing fraud and errors. Blockchain creates a tamper-proof record of each transaction. This boosts trust among all parties involved.
Here are some key benefits of blockchain in supply chain:
- Improved Transparency: All parties can see and verify transactions.
- Enhanced Security: Data is encrypted and immutable.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces paperwork and manual checks.
| Feature | Traditional Supply Chain | Blockchain Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Limited | High |
| Security | Moderate | High |
| Efficiency | Low | High |
Healthcare Applications
Blockchain in healthcare ensures the secure handling of patient records. It provides a decentralized system where data cannot be altered. This increases patient trust and data accuracy. Healthcare providers can access patient history quickly and securely.
Key benefits include:
- Data Security: Patient records are encrypted and safe.
- Interoperability: Easy sharing of data across different healthcare systems.
- Transparency: Patients can track and control their records.
Blockchain can also streamline clinical trials. It ensures data integrity and transparency. This helps in faster and more reliable research outcomes.
Challenges And Limitations
Blockchain technology is a game-changer, but it has its challenges. Understanding these limitations is crucial for effective deployment.
Scalability Issues
One major challenge of blockchain technology is scalability. As the number of users grows, the system can slow down. This affects transaction speeds and increases costs. For example, Bitcoin transactions can take up to 10 minutes. This delay is not ideal for real-time applications.
Another issue is the size of the blockchain. Each transaction adds a new block to the chain. Over time, this makes the blockchain very large. Storing and processing this data requires significant resources.
| Blockchain | Transaction Speed | Block Size |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | 10 minutes | 1 MB |
| Ethereum | 15 seconds | 2 MB |
Regulatory Concerns
Blockchain operates in a gray area of the law. Different countries have different regulations. Some countries welcome it, others restrict or ban it. This inconsistency creates uncertainty for businesses.
Also, blockchain can be used for illegal activities. Money laundering and fraud are concerns. Governments are struggling to create rules. They want to allow innovation but prevent misuse. This balancing act is difficult.
- Money Laundering: Blockchain can obscure illegal transactions.
- Fraud: Scammers use blockchain to trick people.
- Uncertainty: Laws are not clear in many places.
Credit: www.cipe.org
Future Of Blockchain
The future of blockchain promises to revolutionize many industries. This technology continues to evolve rapidly. Let’s explore what lies ahead for blockchain technology.
Emerging Trends
Blockchain is set to transform various fields. Here are some emerging trends:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi platforms offer financial services without intermediaries.
- Blockchain in Supply Chain: It enhances transparency and traceability.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs are changing digital asset ownership.
- Smart Contracts: These contracts execute automatically when conditions are met.
Potential Impact
The impact of blockchain technology is vast. Consider these potential impacts:
| Sector | Impact |
|---|---|
| Finance | Reduced transaction costs and faster settlements. |
| Healthcare | Improved data security and patient privacy. |
| Education | Verifiable academic credentials. |
| Real Estate | Streamlined property transactions. |
Blockchain technology is becoming more integrated into daily life. Its potential is limitless.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing various industries with its secure and transparent nature. Its applications range from finance to healthcare. Embracing blockchain can lead to increased efficiency and trust. Stay ahead by understanding and integrating blockchain into your business strategies. The future of technology lies in this innovative and evolving field.